How are KPI scores calculated?
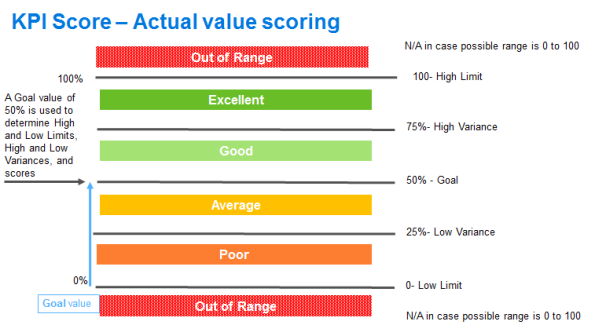
When a KPI is created, the system initially calculates a Goal value, also called a Default Goal, for the KPI that is the average of the upper and lower limit set for the periodicities. You can use the Default Goal calculated by the system or set your own Goals. Refer to the Scorecards Product that assists agents, supervisors and all contact center employees to focus on critical aspects of their performance and identify opportunities for improvement. Administration Guide for information on editing Goals.
Upper and lower limit values can be set to a value between 0 and 100. The difference between the upper and lower values is called the Value Range.
In addition to the Goal, KPI scores are calculated based on:
-
The comparison of the Actual Value (the score is based on the Goal value) or Peer Value (the score is based on the Peer value).
-
The specified upper and lower values.
-
The Upper Variance and Lower Variance.
-
The Variance to Planned setting. The Variance for a KPI can be set to Down or Up. When the variance is set to Down, lower numbers are better. When the variance is set to Up, higher numbers are better.
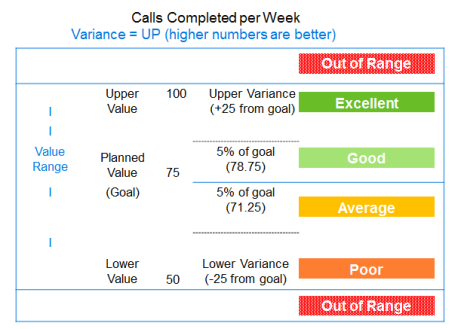
In the following illustration:
-
Goal is 75
-
Variance to Planned is Up
-
Upper Variance is set to +25 from Goal (75 + 25) = 100
-
Lower Variance is set to -25 from Goal (75 - 25) = 50
-
An Excellent score is a score that exceeds the Goal by the variance level or more (over 78.75%)
-
A Good score is a score that meets the Goal at the planned goal or within the variance level toward the direction of the variance (75% to 78.75%)
-
An Average score is a score that is within the variance level, but away from the direction of the variance (from 71.25% up to 75%)
-
A Poor score is a score that missed the goal by more than the allowed variance level (below 71.25%)
-
An Out of Range score is a score that is outside the value range (above 100% or below 50%)
In a KPI with the variance set to Down, Good is within the percentage variance or variance value BELOW the planned value, and Average is in the percentage variance or variance value ABOVE the planned value. See the following example.
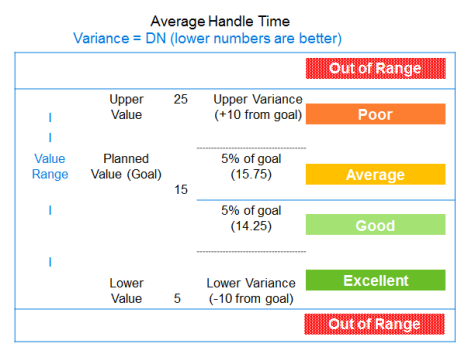
These examples show KPIs that use actual values with goal and upper and lower value ranges. The numbers used here are examples only. Moreover, the examples show the same value range both above and below the planned value. Your ranges might be different.
Peer Value and Actual Value scoring
Use Peer Value scoring when you are not sure what would be realistic actual value goals for a KPI. Using Peer Value scoring in such a case allows you to identify the top or low performers with respect to the peer group. As you gain insights into the group's actual performance, you can switch to Actual Value scoring.
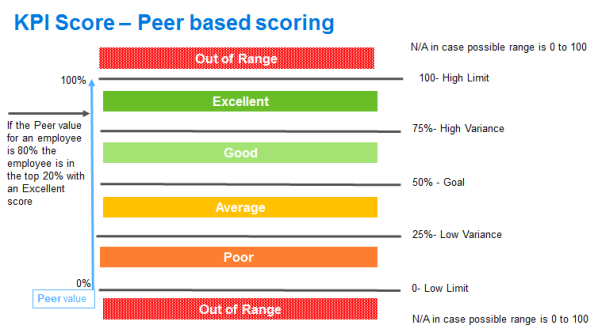
Use Actual Value scoring when you have realistic goals defined. Actual Value scoring allows you to identify the top or low performers with respect to their goals.